7 million deaths worldwide each year, according to the WHO. One of the best solutions? The electrostatic precipitator filter. In today’s world, air quality has become a hot topic. With increasing pollution levels, more people are looking for advanced technologies that can effectively clean the air. Electrostatic Precipitator Filter is a powerful technology which transforming how we think about air purification, particularly in large industrial spaces and HVAC systems.
But what exactly is an electrostatic precipitator filter, and why should you care about it? In this article, we’ll dive deep into the mechanics, benefits, and applications of this remarkable air filtration technology. We’ll also explore how it works, where it’s commonly used, and why it’s becoming an essential part of modern air purification systems.
What is an Electrostatic Precipitator Filter?
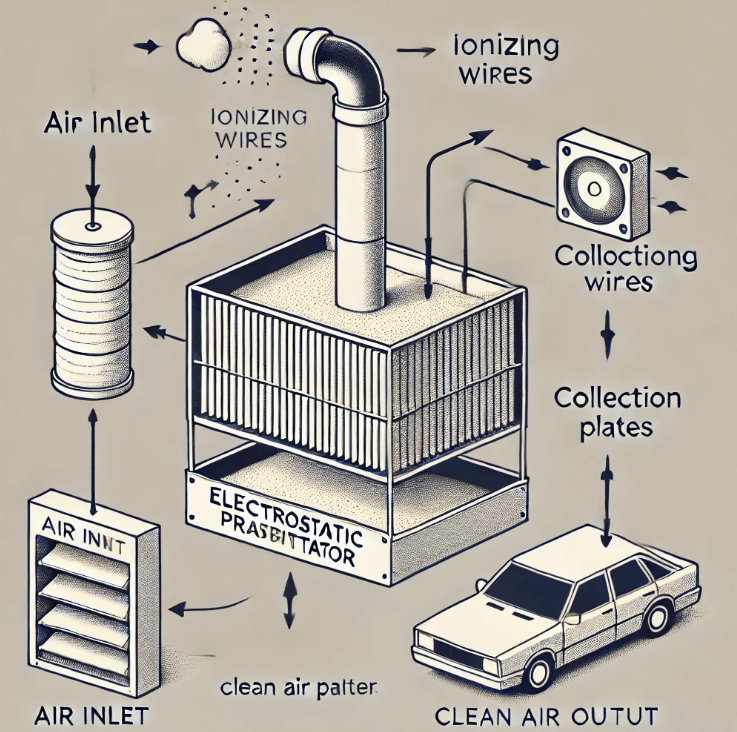
An electrostatic precipitator filter (ESP) is an advanced air-cleaning technology designed to remove fine particles such as dust, smoke, and soot from the air. The filter works by charging particles with electricity, then capturing them on charged plates. This method ensures that even the smallest particles are captured efficiently, making it one of the most effective air purification technologies available today.
How Does It Work?
The working principle of an electrostatic precipitator filter is surprisingly simple yet effective. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Ionization of Particles: As air flows through the system, tiny particles (such as dust, pollen, and smoke) are charged using high-voltage electrodes. The electric charge makes these particles cling to surfaces more easily.
- Collection on Plates: After the particles are charged, they are drawn to oppositely charged collection plates. These plates trap the particles, allowing clean air to pass through the system.
- Regular Cleaning: Over time, the plates gather a significant amount of debris. To maintain the system’s efficiency, the plates need to be cleaned regularly. Many systems offer self-cleaning mechanisms, making maintenance a breeze.
Why Does It Work So Well?
The reason the electrostatic precipitator filter is so effective lies in its ability to capture extremely fine particles. Unlike traditional filters that rely on mechanical filtration, an ESP uses electric fields to attract particles as small as 0.01 microns. This makes it an excellent option for filtering out pollutants like smoke, fine dust, and even bacteria.
The Different Types of Electrostatic Precipitators
1. Plate Precipitator
The plate electrostatic precipitator is one of the most common types. It consists of parallel plates with high-voltage wires placed between them. As the polluted air passes through the plates, particles are charged by the ionizing wires. These charged particles then migrate to the plates, where they are collected and removed periodically.
- Applications: Plate precipitators are typically used in industrial processes like coal-fired power plants, cement factories, and steel mills.
- Key Feature: Their ability to handle large volumes of gas makes them ideal for heavy industries.
2. Dry Electrostatic Precipitator
Dry electrostatic precipitators are mainly used in environments where the particles collected are dry and non-sticky. This makes them suitable for industries that emit dust, such as cement plants or power stations. The particles are collected on plates and can be easily removed by rapping or vibration.
- Applications: Dust collection in industrial settings.
- Key Feature: Requires less cleaning and maintenance as the particles are dry.
3. Wet Electrostatic Precipitator
Wet electrostatic precipitators (WESP) are used when the particles are sticky, moist, or corrosive. These precipitators use water to clean the plates, ensuring that the collected particles do not accumulate and clog the system. They are often found in industries that produce fine mists or have high moisture content in their emissions.
- Applications: Used in pulp and paper mills, chemical processing plants, and other industries where wet, sticky particulates are prevalent.
- Key Feature: High efficiency in capturing fine mist particles and sticky pollutants.
4. Tubular Precipitator
A tubular precipitator features cylindrical tubes instead of plates. Air flows through these tubes, where the particles are charged and collected on the walls of the tubes. This design is particularly useful for capturing sticky or fibrous materials.
- Applications: Oil refineries, waste incinerators, and industries producing aerosols.
- Key Feature: Efficient at handling complex pollutants such as tar and mist.
Electrostatic Precipitator Working Principles
The working principle of an electrostatic precipitator filter is based on the process of ionization. Here’s a step-by-step explanation:
- Ionization: As polluted air enters the precipitator, it passes through high-voltage electrodes, which ionize the air. This ionization process imparts an electrical charge to the dust particles.
- Particle Attraction: Once charged, these particles are drawn to oppositely charged collection plates or tubes. This is similar to how static electricity makes dust stick to surfaces.
- Collection: The particles adhere to the collection surfaces, and clean air is allowed to pass through.
- Removal: Periodically, the collection surfaces are cleaned. In dry precipitators, this is done by shaking or rapping the plates, while in wet precipitators, water is used to wash away the accumulated particles.
This simple yet highly effective process allows electrostatic precipitator filters to remove up to 99% of particulate matter from the air.
Efficiency of Electrostatic Precipitator
The efficiency of an electrostatic precipitator filter largely depends on the design and the nature of the particles being removed. In general, ESPs can remove particles as small as 0.01 microns with an efficiency ranging from 90% to 99%. Several factors can influence the efficiency:
- Particle Size: Smaller particles are harder to capture, but ESPs are still highly efficient in filtering out fine particles like smoke and bacteria.
- Gas Flow Rate: The speed at which the gas passes through the precipitator can affect particle capture. Slower flow rates generally result in higher efficiency.
- Voltage: The strength of the electric field plays a key role in charging the particles. Higher voltage generally leads to better performance.
History of Electrostatic Precipitators
The electrostatic precipitator was invented in 1907 by Dr. Frederick G. Cottrell, a chemistry professor. Initially, it was used to reduce acid mist emissions from the lead smelting process. As industries expanded and environmental concerns grew, the application of ESP technology became more widespread.
- Early Adoption: Power plants and cement factories were some of the earliest adopters of electrostatic precipitators.
- Growth in Popularity: During the 20th century, the increasing focus on environmental pollution led to more industries integrating ESPs into their operations to reduce particulate emissions.
- Modern Advancements: Today, advancements in technology have made ESPs more efficient, with the ability to capture even finer particles. They are now used in everything from industrial applications to residential HVAC systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electrostatic Precipitators
Advantages
- High Efficiency: ESPs can capture extremely fine particles, including dust, smoke, and even bacteria, which traditional filters might miss.
- Low Operating Costs: Once installed, electrostatic precipitator filters are relatively inexpensive to operate. They don’t require frequent filter replacements, making them cost-effective in the long run.
- Environmentally Friendly: Unlike mechanical filters, ESPs don’t generate waste from disposable filters, making them a greener choice for air purification.
- Energy Efficient: Because ESPs don’t physically block airflow, they allow HVAC systems to work more efficiently, reducing energy consumption.
Disadvantages
- Initial Cost: ESP systems can be more expensive to install than traditional filters. However, the low operating costs usually offset this initial investment over time.
- Maintenance: While ESPs don’t require frequent filter changes, the collection plates must be cleaned regularly. Failure to maintain them can result in reduced efficiency.
- Limited Odor Removal: While ESPs are excellent at capturing particles, they are not as effective at removing gases and odors. Additional filtration may be required to address these issues.
Benefits of an Electrostatic Precipitator Filter
Now that you understand how it works, let’s talk about why you should consider investing in an electrostatic precipitator filter for your home or business. Here are some of the main benefits:
- Highly Efficient Particle Removal: Whether you’re dealing with dust, pollen, or smoke, ESPs can capture up to 99% of airborne particles.
- Low Maintenance Costs: Unlike traditional air filters, which require frequent replacement, electrostatic precipitator filters are easy to clean and maintain. This means you’ll save money on filter replacements over time.
- Environmentally Friendly: Since ESPs don’t require disposable filters, they generate less waste, making them a greener option for air purification.
- Energy Efficient: With low energy consumption, ESPs are an eco-friendly choice for both residential and industrial applications.
- Odor Reduction: While they excel at capturing particles, electrostatic precipitator filters also help reduce odors in the air, making your environment more pleasant.
Applications of Electrostatic Precipitator Filters
Industrial Use
The electrostatic precipitator filter is commonly used in industrial settings where large amounts of pollutants are generated. Factories, power plants, and manufacturing facilities benefit from these filters by removing harmful particles from the exhaust before releasing air into the environment. This not only helps reduce air pollution but also ensures that industries comply with environmental regulations.
For example, power plants often produce significant amounts of ash and soot, which can be hazardous if released into the atmosphere. By using an ESP, these plants can capture the particles and prevent them from contaminating the air.
Residential and Commercial HVAC Systems
In residential and commercial buildings, air quality is crucial for maintaining a healthy environment. Electrostatic precipitator filters are increasingly being integrated into HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems to keep indoor air free from pollutants.
With the ability to capture fine particles, these filters are particularly beneficial for people with respiratory conditions such as asthma or allergies. The electrostatic air cleaner in an HVAC system ensures that the air circulating throughout the building is clean and free of allergens.
Medical Facilities
Hospitals and clinics are another area where electrostatic precipitator filters play a significant role. Maintaining sterile and clean air is crucial in medical facilities to prevent the spread of infections. ESPs help remove airborne pathogens like bacteria and viruses, creating a safer environment for patients and staff.
Automotive Industry
Did you know that electrostatic filters are also used in cars? Yes, certain high-end car models integrate ESPs to ensure that the air circulating inside the vehicle is purified. This helps reduce exposure to exhaust fumes and other pollutants while driving.
Maintenance of Electrostatic Precipitator Filters
One of the significant advantages of electrostatic air filters is their relatively low maintenance. However, proper upkeep is essential to ensure they continue functioning efficiently. Here’s how to maintain them:
- Regular Cleaning of Collection Plates: The collection plates can gather a significant amount of dust and particles over time. Cleaning them every 3 to 6 months ensures optimal performance.
- Inspecting Electrical Components: The ionizing wires or electrodes should be checked periodically to ensure they’re functioning correctly. Damaged components can reduce the effectiveness of the filtration process.
- Self-Cleaning Models: Some electrostatic precipitator filters come with automatic cleaning functions, which reduce the need for manual maintenance. These models may use water or brushes to clean the collection plates automatically.
Electrostatic Precipitator Filters vs. Traditional Filters
You might wonder how an electrostatic precipitator filter compares to traditional mechanical filters. While both serve the purpose of purifying air, they differ in several key areas:
- Efficiency: While mechanical filters are effective at capturing larger particles, ESPs excel at capturing microscopic particles like smoke and bacteria, making them a better choice for high-efficiency air purification.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Traditional filters need to be replaced frequently, leading to ongoing costs. In contrast, electrostatic filters only need cleaning, making them a more cost-effective long-term solution.
- Airflow: Electrostatic precipitator filters allow for better airflow since they don’t physically block particles in the same way as mechanical filters. This means HVAC systems don’t have to work as hard, which can reduce energy consumption.
Conclusion
Air quality concern is growing so electrostatic precipitator filters are becoming an essential part of modern air purification. To reduce pollution in an industrial setting or improve air quality in your home, these filters offer a highly efficient and cost-effective solution. Their ability to capture even the smallest particles sets them apart from traditional filtration methods, making them the go-to choice for clean air.
As industries and homes continue to prioritize health and environmental sustainability, the electrostatic precipitator filter is positioned to play a pivotal role in ensuring cleaner air for everyone. Whether in HVAC systems, medical facilities, or power plants, this technology is shaping the future of air purification, one particle at a time.
FAQ on Electrostatic precipitator filters
What is the principle of an electrostatic filter?
An electrostatic filter works by using electrical charges to remove dust, particles, and other airborne contaminants from the air. It ionizes the particles, giving them an electrical charge, and then attracts them to plates with an opposite charge, trapping them for removal.
What is the use of an ESP filter?
An Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) filter is used to control and reduce air pollution by removing particulate matter such as dust, smoke, and fine pollutants from gas streams in industries, power plants, and even residential HVAC systems.
What is the purpose of an electrostatic precipitator?
The primary purpose of an electrostatic precipitator is to clean polluted air by removing harmful particles, thereby improving air quality and reducing environmental pollution. It is especially useful in industries where the emission of particulate matter is a concern.
How do electrostatic filters work?
Electrostatic filters work by creating an electric field that charges particles in the air. The charged particles are then attracted to and collected on oppositely charged plates or surfaces, leaving the air cleaner and free of pollutants.
What is the working principle of a filter?
The working principle of most filters is to separate unwanted substances from a fluid (air or liquid) by passing it through a porous material or a surface that traps contaminants while allowing the clean medium to pass through.
What are the principles of an electrostatic precipitator?
The main principles of an electrostatic precipitator include ionization, particle charging, migration to collection surfaces, and periodic removal of collected particles. These processes ensure efficient removal of dust and particulate matter from gas streams.
What is the working principle of ESP?
The working principle of an ESP involves ionizing the particles in a gas stream by passing them through an electric field, then collecting the charged particles on electrodes. Once enough particles accumulate, they are removed, leaving the gas cleaner.
What is the objective of an electrostatic precipitator?
The objective of an ESP is to reduce air pollution by efficiently removing fine particles like dust, smoke, and other pollutants from industrial emissions, ensuring cleaner air and compliance with environmental regulations.
What is the spark rate in ESP?
The spark rate in an ESP refers to the frequency of electrical sparks that occur between the electrodes. A controlled spark rate is necessary to optimize the removal of particulate matter, but excessive sparking can indicate operational issues.
How do you clean ESP filters?
ESP filters are cleaned by periodically removing the collected particles from the plates. In dry ESPs, this is done by shaking or rapping the plates to dislodge the dust, while in wet ESPs, water is used to wash the plates clean. Regular maintenance is essential to keep the system running efficiently.
DheerajSonwane is a dedicated writer with expertise in air purification technologies. He focuses on providing well-researched content to help readers improve indoor air quality in homes and businesses. As the lead writer at AirPurifierMaster.com, Dheeraj offers practical advice his insightful reviews guide individuals in choosing the best air purifiers for their needs.

